Best Books to Read in 2023
Best Books to Read in 2023 Are you a bookworm or a bibliophile, if yes, then this is the ...
IIT Mandi researchers led by Dr. Dericks Praise Shukla and his PhD student Ms. Harsimranjit Kaur Romana have derived concerning insights into human activity-induced groundwater pollution, particularly through agricultural runoff in Punjab.
Dr. Dericks Praise Shukla is an Associate Professor, School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, IIT Mandi and Harsimranjit Kaur Romana is a native of Punjab.
 Punjab
PunjabPunjab, as with most agriculture-centric states of India, has experienced a profound shift in its crop patterns over the last half-century, primarily due to the Green Revolution, say IIT Mandi researchers.
This transformation has led to the dominance of mono-cropping of high-yielding varieties of rice and wheat, making Punjab the second-largest contributor to wheat production in India, say IIT Mandi researchers.
Unfortunately, these intensive agricultural practices have resulted in severe groundwater exploitation, with over 74% of the irrigation requirements being met through groundwater in the absence of good monsoon.
In the last two decades, the groundwater demand has increased due to the absence of monsoon. The depth of groundwater wells has increased due to the lowering of groundwater levels as a result the quality of groundwater is continuously deteriorating, say IIT Mandi researchers.
Also read – Top BMS Colleges in Odisha
The groundwater department and local farmers have to exploit groundwater from deeper geological strata which are enriched in heavy metals and few are radioactive having serious health impacts.
The prolific agricultural activity has come at a significant cost – groundwater pollution. Since 94% of the population of Punjab relies on groundwater for their drinking water needs, the pollution of groundwater has resulted in serious health issues.
Punjab once celebrated as the “bread bowl of India”, is now infamously referred to as the “cancer capital” of India, reflecting the dire consequences of water pollution and its impact on human health, say IIT Mandi researchers.
While multiple studies have highlighted groundwater quality issues in India, an extensive time-based and place-based analysis of the region has been lacking. The IIT Mandi study sought to address this critical gap.
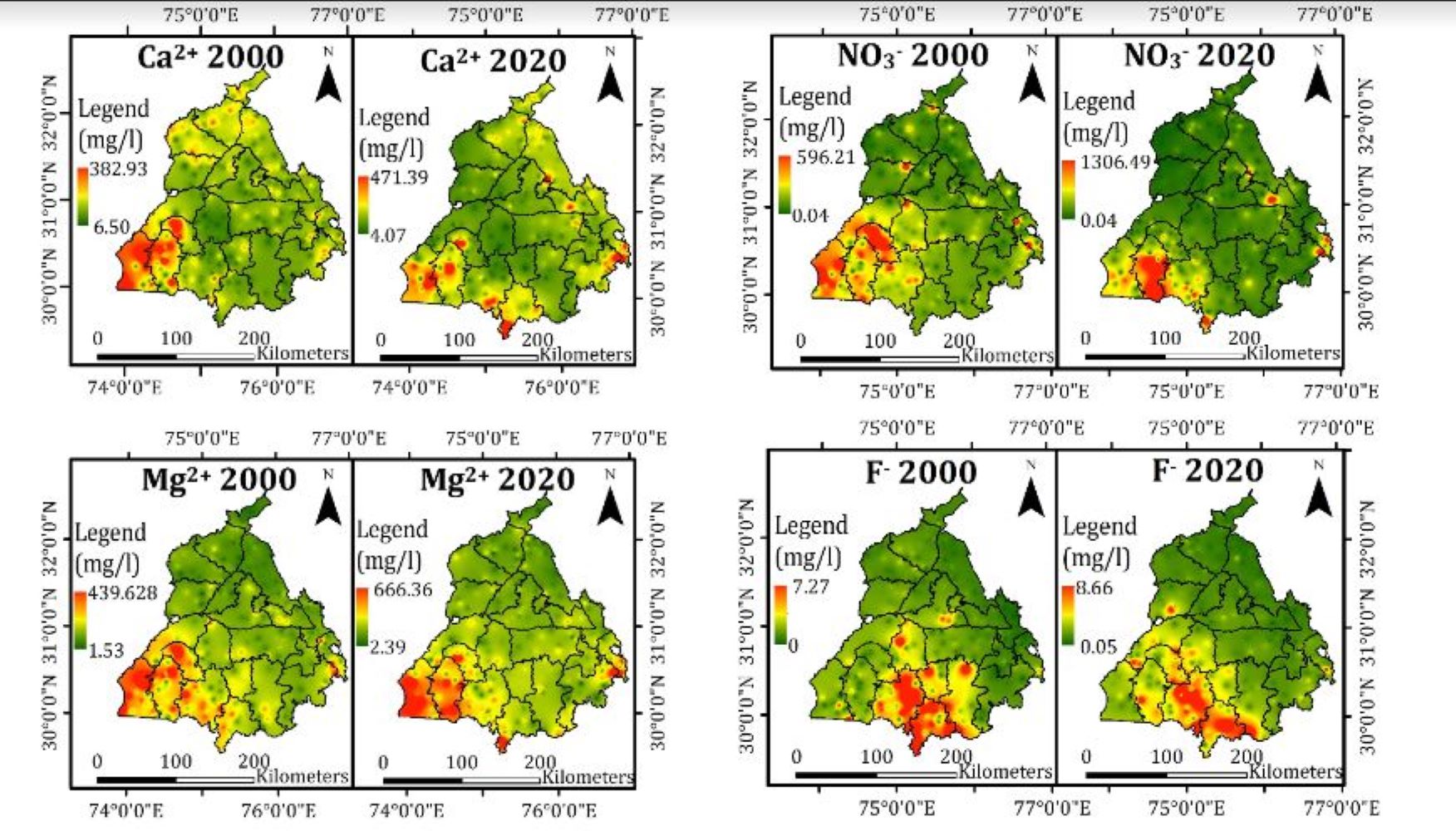
Explaining the motive of the study, Dr. D.P. Shukla, Associate Professor, School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, IIT Mandi, said they aimed to assess how groundwater quality for drinking purposes changed from 2000 to 2020 at different places.
It also sought to examine ten-year trends in health hazards associated with contaminants like nitrate and fluoride, along with identifying regions with notably subpar groundwater quality, he said.
 Findings of IIT Mandi researchers
Findings of IIT Mandi researchersThe findings of this comprehensive research have been published in the journal “Environmental Science and Pollution Research”.
The paper was co-authored by Ms. Harsimranjit Kaur Romana, Prof. Ramesh P. Singh, and Dr. Dericks Praise Shukla. The paper may be accessed here: ‘https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29200-6’
The study by IIT Mandi researchers involved the measurements of pH, electric conductivity (EC), and various ions from over 315 sites in Punjab. The results revealed a disturbing trend, with water quality declining in the southwestern region of Punjab, adversely affecting the health of the residents.
In contrast, the north-eastern regions, nourished by Himalayan rivers, exhibited comparatively better water quality.
This study by IIT Mandi researchers not only sheds light on the alarming state of groundwater pollution in Punjab but also serves as a crucial resource for policymakers.
It underscores the urgent need for mitigation measures and creates awareness among residents about the locations with unsafe groundwater for drinking.
These findings emphasize that immediate attention of the state government is required to investigate the quality of groundwater for drinking and irrigation purposes.
The study’s insights are expected to catalyze actions aimed at safeguarding this invaluable resource and the health of the population, say IIT Mandi researchers.
 About IIT Mandi
About IIT MandiIIT Mandi has nine Academic Schools and five major Research Centers. The Schools are the School of Biosciences and Bioengineering (SBBE), School of Chemical Sciences (SCS), School of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences (SMSS), School of Physical Sciences (SPS), School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering (SMME).
The others are School of Civil and Environmental Engineering (SCENE), School of Computing and Electrical Engineering (SCEE), School of Humanities and Social Sciences (SHSS), and School of Management (SOM).
The Centers are Advanced Materials Research Centre (AMRC), Centre for Design and Fabrication of Electrical Devices (C4DFED), BioX Centre, Indian Knowledge System and Mental Health Applications Centre (IKSMHA Centre) and Centre for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics.
S Vishnu Sharmaa now works with collegechalo.com in the news team. His work involves writing articles related to the education... (Full bio)

Best Books to Read in 2023 Are you a bookworm or a bibliophile, if yes, then this is the ...

In the exhilarating journey of 10 Proven Memorize Techniques for Students learning, memory is your trusty companion. Whether ...

Top 20 toughest exams in world is about exams in the world that required very hard work to ...
Top 20 toughest exams in India - Exams are the perhaps most toughest moments for any student. A ...

Top 20 Colleges of DU Getting admissions to the top 20 colleges of DU is a dream for every ...
Top 20 NITs of India - Amongst the 31 NITs in India, today, we are talking ...

Here are the Top 12 Artificial Intelligence in Mumbai. Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human ...

As you stand on the Best Science Courses after 12th academic journey, the realm of science beckons, offering ...
Millions of students have entrusted CollegeChalo to facilitate their seamless and smooth admission process to their dream colleges and universities. With CollegeChalo, you can gain a competitive edge by easily accessing exam and course details to stay ahead of the admission journey. What are you waiting for?
Search your dream college